2024-02-28
Exposure to ethylene oxide and the risk of periodontitis
Dentistry
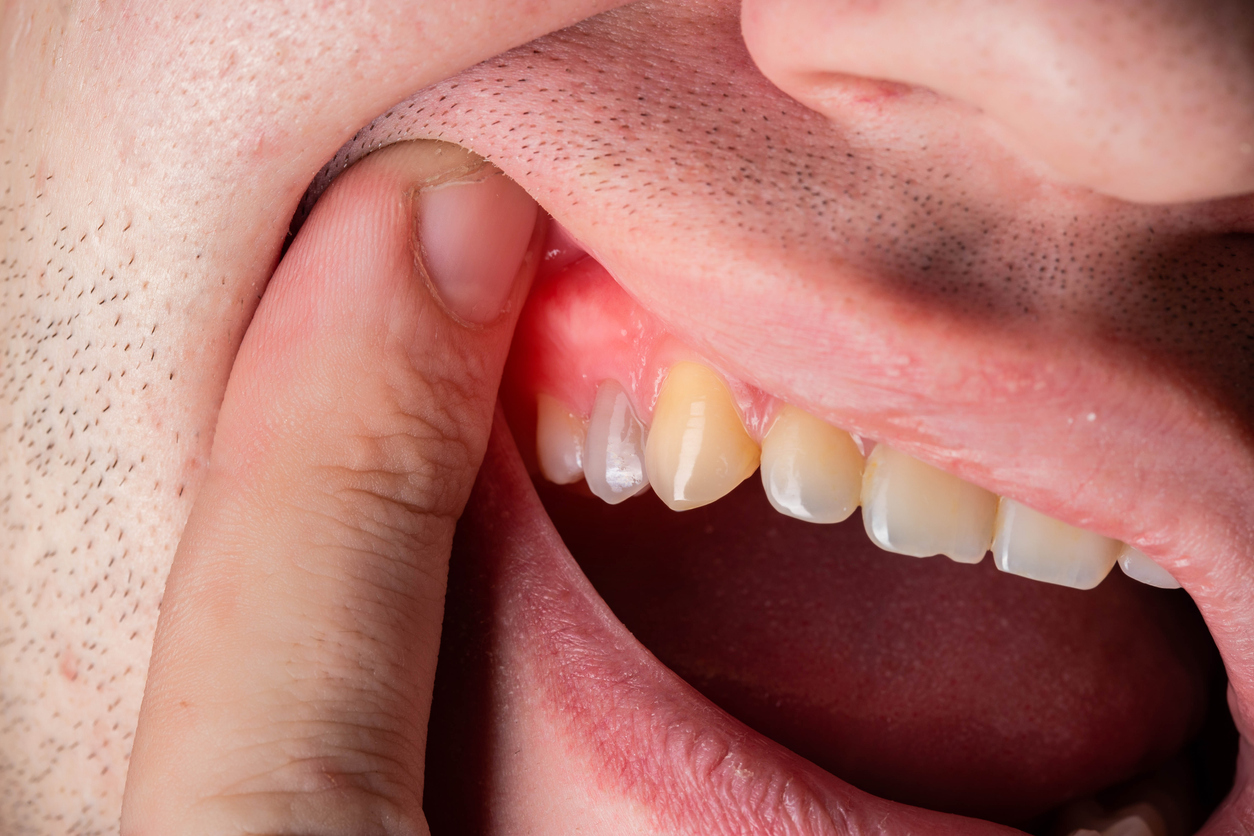
The pathological mechanisms of periodontitis seem to involve environmental exposures. In this study, researchers explored the case of exposure to ethylene oxide. A total of 1,065 participants, aged over 30, were recruited from the 2013-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Participants with the highest levels of ethylene oxide adducts with hemoglobin had an increased risk of periodontitis, after adjusting for all covariates. The level of ethylene oxide adducts with hemoglobin was significantly associated with four inflammatory mediators, suggesting an involvement of inflammation in the links between ethylene oxide and periodontitis.
Last press reviews
Mood, memory, inflammation—could it all happen on the plate?

#Microbiota #Depression #Alzheimer #Neuroinflammation #AntiInflammatory...
Purple on your plate, benefits in your cells?

#Anthocyanins #OxidativeStress #Microbiota #CardiovascularHealth #Bioav...
