2024-06-13
Plant extracts, a natural alternative to existing treatments for hair loss
Dermatology and Venereology
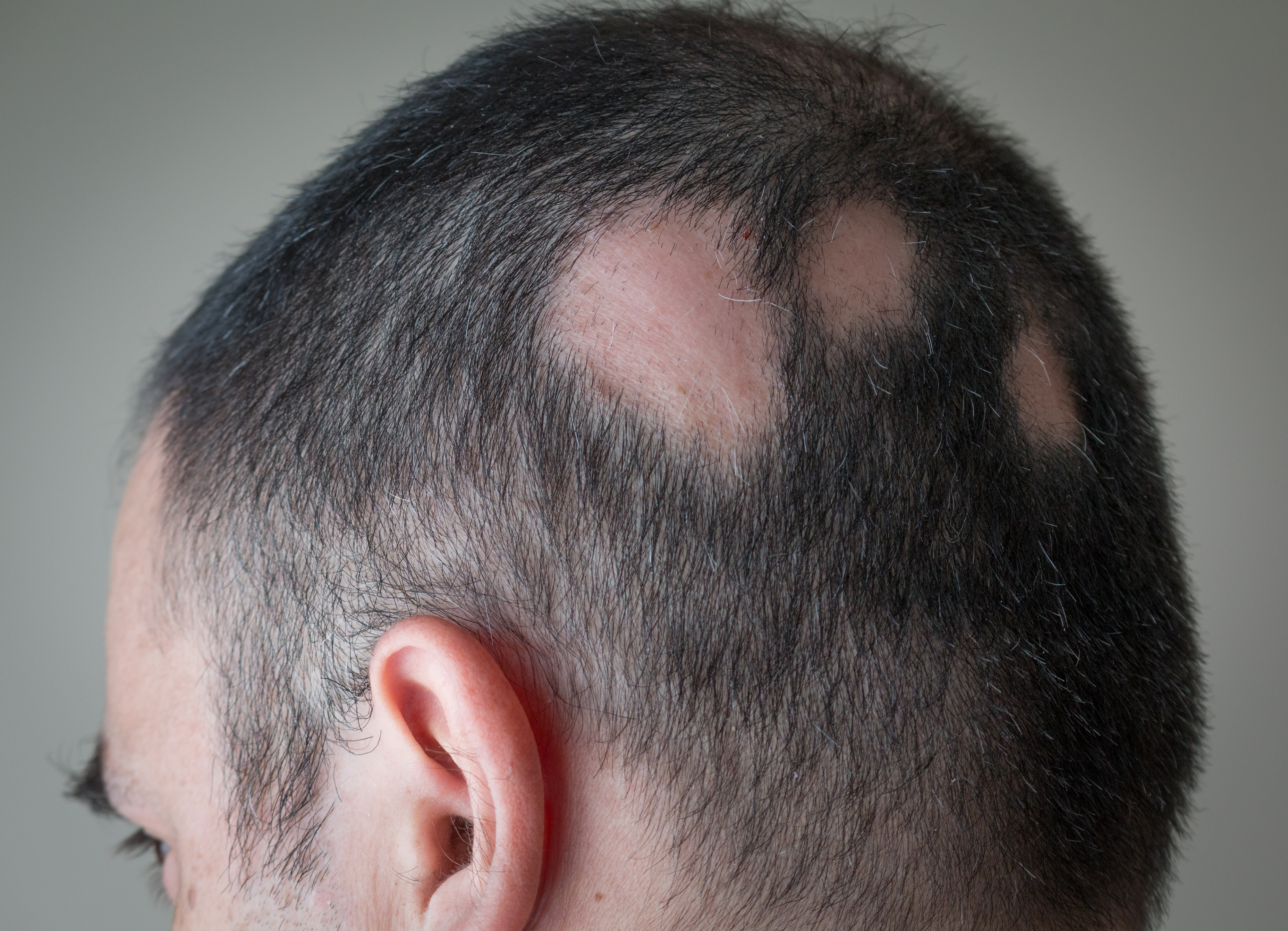
Hair loss, known as alopecia, can affect any part of the body.
In this study, researchers investigated the effects of various plant extracts on alopecia.
The pharmacological effects of plant extracts were associated with the promotion of cell survival, cell proliferation and cell cycle progression. They have also been associated with the increase of several growth factors such as IGF-1, VEGF, HGF and KGF (FGF-7).
The efficacy of these extracts has been confirmed in clinical trials. These clinical trials showed an increase in hair density and hair shaft diameter.
Active compounds identified included phenolics, terpenes, terpenoids, sulfur compounds and fatty acids.
In addition, oxidative stress, inflammation, cellular senescence and apoptosis were attenuated, and male hormones were down-regulated. Entry into the telogen phase of the hair cycle was thus prevented.
These plant extracts and phytochemicals stimulated cell signalling pathways mediated by protein kinase B (PKB, also known as AKT), extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK), Wingless and Int-1 (WNT), or Sonic Hedgehog (SHH). Other cell signaling pathways were suppressed, notably those mediated by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β or bone morphogenetic protein (BMP).
These results suggest that plant extracts and their active compounds may have beneficial effects on hair health. The discovery of phytochemicals targeting these cellular events and signaling pathways could facilitate the development of new targeted therapies for alopecia.
The combination of different plant extracts and phytochemicals could offer a natural alternative to chemical treatments for hair loss, bringing comfort and convenience to people who prefer to avoid synthetic drugs.
In conclusion, this article suggests that plant extracts have significant potential to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth, offering natural alternatives to existing treatments.
Future studies should focus on discovering new active compounds and optimizing formulations to maximize therapeutic effects while minimizing side effects.
Last press reviews
Birch allergy: could one shot change everything?

#AllergicRhinoconjunctivitis #IgG4 #Allergoid #BirchPollen #Immunotherap...
Allergies: could the gut hold the key?

#SeasonalAllergicRhinitis #Probiotics #Prebiotics #GutMicrobiota...
Parkinson’s disease: bone health shouldn’t be overlooked

#ParkinsonsDisease #Osteoporosis #FractureRisk #FRAX #Prevention...