2024-11-07
Memory Immunity Against COVID-19: A Less Effective Response in Organ Transplant Recipients?
Infectiology
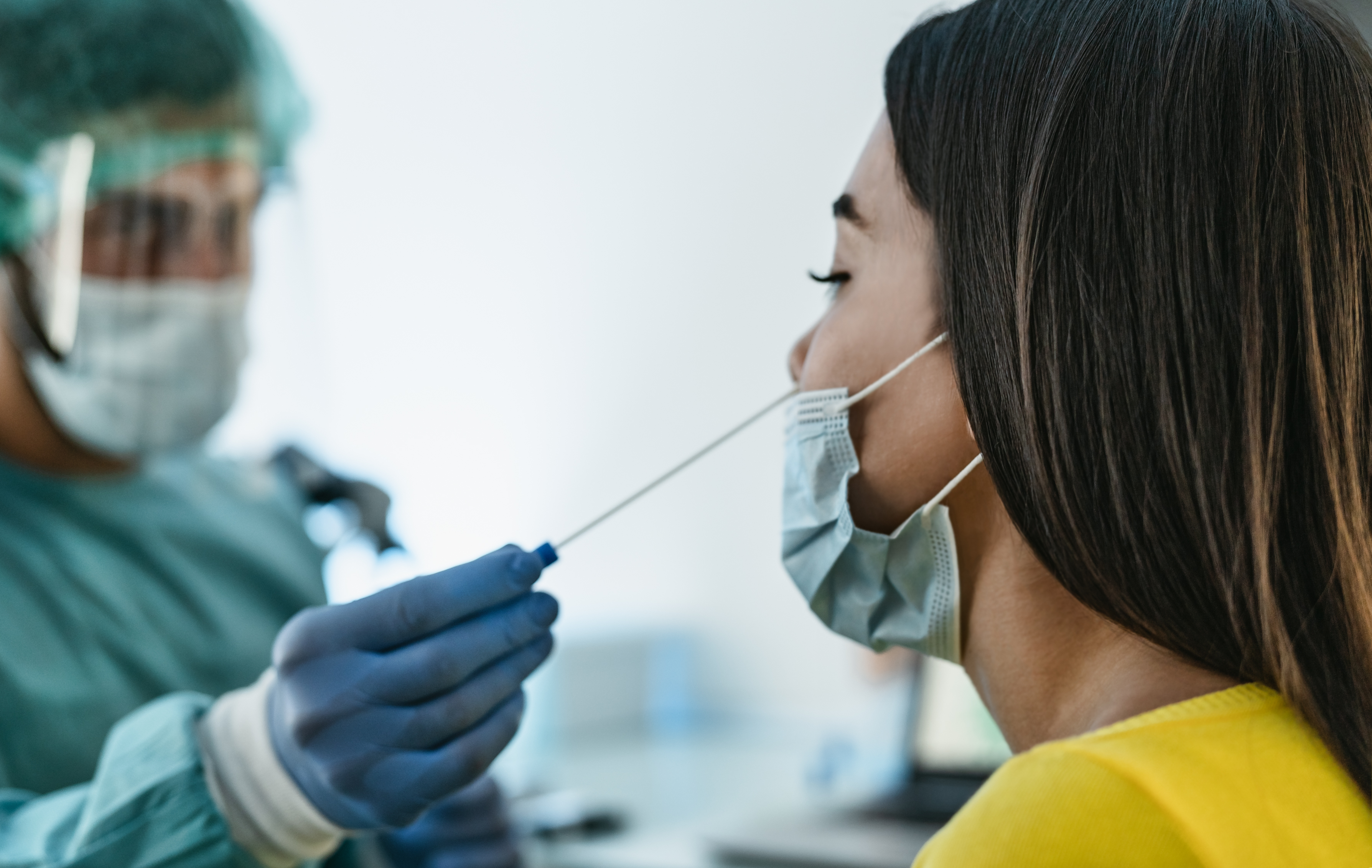
Vaccination against COVID-19 has transformed
the fight against the pandemic. However, the immune response to vaccination is
not uniform across all individuals. Solid organ transplant recipients are among
the high-risk groups for severe COVID-19 due to their weakened immune systems,
compromised by immunosuppressive medications required to prevent graft
rejection. This study examines the role of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory B cells
in post-vaccination immunity, assessing their capacity to induce a protective
response in this vulnerable population.
Comparative
Study in Transplant Patients and Immunocompetent Individuals
The study analyzed immune responses in 148 organ transplant recipients and 32
immunocompetent individuals who received multiple booster doses. Concurrently,
a randomized controlled trial (RCT) was conducted with 25 transplant patients
who had not developed neutralizing antibodies (NAb) after three vaccine doses. Two
immunosuppressive strategies were compared:
The results of this study indicated that:
- Standard exposure ;
- Reduced exposure to calcineurin inhibitors.
The results of this study indicated that:
- Transplant recipients show a weaker and delayed memory immune response (after the fourth dose) compared to immunocompetent individuals;
- SARS-CoV-2-specific memory B cells are strongly correlated with neutralizing antibody levels;
- SARS-CoV-2-specific memory B cells and IL-2-producing T cells serve as strong predictive markers for seroconversion and protection against severe COVID-19 in transplant recipients;
- Shifting from a standard to a reduced immunosuppressive strategy supports a more robust and faster immune response after the fourth vaccine dose.
Key Role
of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Memory B Cells in Protecting Transplant Patients Against
COVID-19
This study highlights the central role of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory B cells in
protecting organ transplant recipients from COVID-19. It also confirms that
adjusting immunosuppressive treatments could enhance vaccination efficacy in
these at-risk patients. Future studies on alternative immunosuppression
regimens and/or adapted vaccination strategies may offer solutions for better
immune protection, particularly by promoting long-term immunity in at-risk
patients.
Last press reviews
Vaccine vs. SMC: rivals or partners?

#MalariaVaccine #R21MatrixM #Malaria #Vaccination #SMC #InsecticideTreat...
A race against time for a vaccine?

#PfSPZ #Vaccination #Malaria #Immunogenicity <br><br><br>...
Birch allergy: could one shot change everything?

#AllergicRhinoconjunctivitis #IgG4 #Allergoid #BirchPollen #Immunotherap...