2025-01-16
Double Protection: The RSV + Flu Vaccine Combo to Boost Seniors' Health
Infectiology
Respiratory infections pose a major health challenge for older adults,
whose immune systems are often weakened, making these infections more severe
and potentially life-threatening. The two main seasonal viruses responsible are
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and the influenza virus.
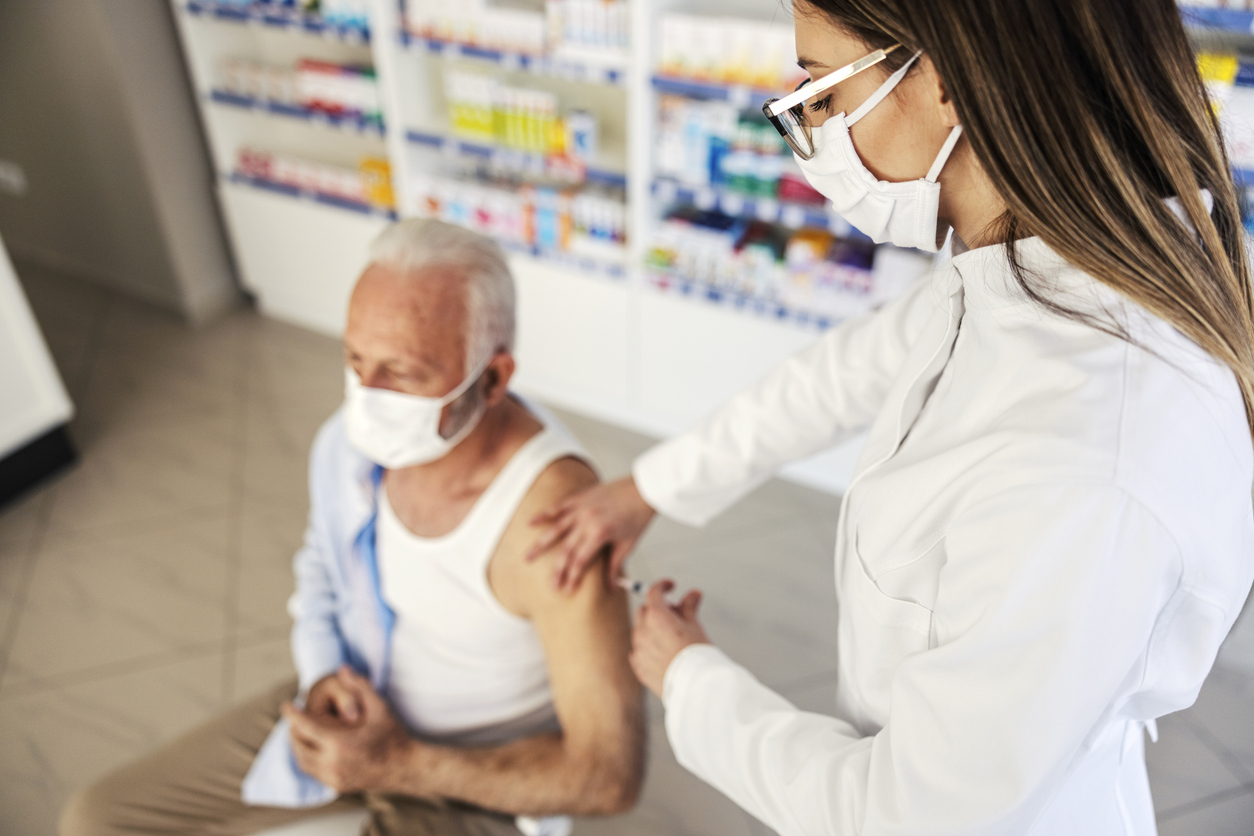
RSV is a leading cause of severe respiratory illnesses, as is the flu, which can lead to serious complications, including pneumonia. Due to their vulnerability, adults aged 65 and older require enhanced protection against these infections.
The development of combination vaccines, allowing the simultaneous administration of two vaccines, offers an innovative and practical solution to improve vaccination rates in this population. This study examines the impact of co-administering a bivalent RSV vaccine (RSVpreF) with the inactivated influenza vaccine (SIIV) in adults aged 65 and older. The goal is to assess not only the safety and tolerance of this combination but also its immune effectiveness compared to separate administration of the two vaccines.
The primary objective was to compare the immune responses, efficacy, tolerance, and safety of co-administration. Key parameters studied included antibody titers against RSV and the flu, as well as local side effects (injection site pain) and systemic effects (fatigue, headaches).
The results showed that the co-administration of the two vaccines was safe and well-tolerated by participants. No vaccine-related serious adverse events were reported. Local and systemic side effects were primarily mild to moderate. Neutralizing antibody titers for RSV and hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers for the flu met predefined non-inferiority criteria. These findings indicate that the immune response to each vaccine, when administered together, is comparable to that achieved with separate administrations.
While these results propose co-administration as an effective and safe solution to protect older adults, future studies will need to evaluate the durability of these immune responses and confirm the impact of this approach on reducing severe respiratory illnesses in this population. Combining the two vaccines could transform the preventive management of respiratory infections in seniors, thereby improving their overall health.
RSV is a leading cause of severe respiratory illnesses, as is the flu, which can lead to serious complications, including pneumonia. Due to their vulnerability, adults aged 65 and older require enhanced protection against these infections.
The development of combination vaccines, allowing the simultaneous administration of two vaccines, offers an innovative and practical solution to improve vaccination rates in this population. This study examines the impact of co-administering a bivalent RSV vaccine (RSVpreF) with the inactivated influenza vaccine (SIIV) in adults aged 65 and older. The goal is to assess not only the safety and tolerance of this combination but also its immune effectiveness compared to separate administration of the two vaccines.
RSVpreF and flu vaccine: an effective solution for seniors?
In this study, 1,403 participants aged 65 and older were randomly assigned to two groups:- A group receiving both vaccines simultaneously (RSVpreF + SIIV);
- A group receiving the vaccines separately, 28 days apart.
The primary objective was to compare the immune responses, efficacy, tolerance, and safety of co-administration. Key parameters studied included antibody titers against RSV and the flu, as well as local side effects (injection site pain) and systemic effects (fatigue, headaches).
The results showed that the co-administration of the two vaccines was safe and well-tolerated by participants. No vaccine-related serious adverse events were reported. Local and systemic side effects were primarily mild to moderate. Neutralizing antibody titers for RSV and hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers for the flu met predefined non-inferiority criteria. These findings indicate that the immune response to each vaccine, when administered together, is comparable to that achieved with separate administrations.
Double vaccine, double protection
This study suggests that the co-administration of RSVpreF and flu vaccines could be a promising option for older adults. It not only offers comprehensive protection against these two significant respiratory infections but also reduces the number of doctor visits. Simplifying this process could increase vaccination rates, which is particularly crucial for this high-risk population.While these results propose co-administration as an effective and safe solution to protect older adults, future studies will need to evaluate the durability of these immune responses and confirm the impact of this approach on reducing severe respiratory illnesses in this population. Combining the two vaccines could transform the preventive management of respiratory infections in seniors, thereby improving their overall health.
Last press reviews
Vaccine vs. SMC: rivals or partners?

#MalariaVaccine #R21MatrixM #Malaria #Vaccination #SMC #InsecticideTreat...
A race against time for a vaccine?

#PfSPZ #Vaccination #Malaria #Immunogenicity <br><br><br>...
Birch allergy: could one shot change everything?

#AllergicRhinoconjunctivitis #IgG4 #Allergoid #BirchPollen #Immunotherap...